NASA/JAXA’s XRISM Mission Captures Unmatched Data With Just 36 Pixels
NASA/JAXA’s XRISM Mission Captures Unmatched Data With Just 36 Pixels
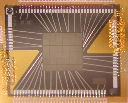
science.nasa.gov
NASA/JAXA’s XRISM Mission Captures Unmatched Data With Just 36 Pixels - NASA Science

NASA/JAXA’s XRISM Mission Captures Unmatched Data With Just 36 Pixels

NASA/JAXA’s XRISM Mission Captures Unmatched Data With Just 36 Pixels - NASA Science
